Rappi Funding History and Risks
 Nan Wang
Nan Wang
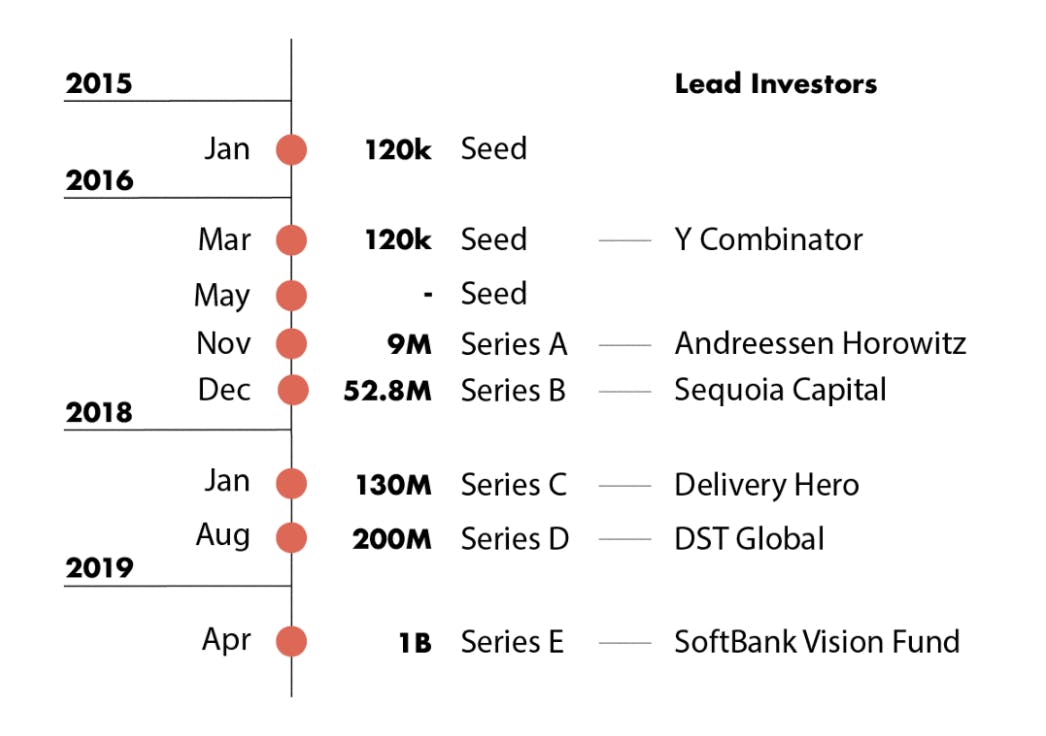
Funding history
Risks
Higher competitive pressure: Due to the hyper-local network effect, it’s highly likely for on-demand delivery to settle into a duopoly market structure. This means being the top 2 players in each country is critical for Rappi to build a profitable business.
In addition to fighting with iFood in Brazil, Uber Eats in Mexico in the food category, to expand into adjacent verticals, Rappi also faces more established players such as Decolar, Hotel Urbano and Mercado Libre in travel and e-commerce.
Higher competitive pressure would result in a lower take rate, higher customer acquisition costs and higher churn.
Labor cost
Rappi might pass on some of the cost increase to customers and merchants in the form of higher commissions. This would negatively affect order volumes.
The concentration of supply: The power-law distribution in the restaurant is extreme. Key accounts (i.e., restaurants with the highest number of transactions) contribute towards the majority of the platform’s GMV. This implies that, firstly, larger restaurants have higher bargaining power and would pay a lower take rate; Secondly, many riders already know which restaurants generate most orders. To make more money per hour, the riders would be near to restaurants with the most orders and do back and forth trips around these popular restaurants. This is an organic way of optimizing the fleet without any AI/ML.
Higher CAC: Rappi is investing a lot of capital into customer acquisition, with the view that LTV will be higher as the company cross-sells into higher-margin, lower frequency verticals. However, industry data shows that churn can be as high as 40- 50% per month for on-demand platforms. If Rappi fails to meaningfully expand into adjacent verticals, Rappi would be capital inefficient in sustaining growth.
Tightening regulation: This year, Rappi and Uber Eats have won the first round of dispute against iFood about restricting restaurants working with other platforms. CADE (the Administrative Council for Economic Defense) said it has forbidden delivery app iFood to sign new exclusivity deals with restaurants for delivery as a way to preserve competition. If regulators prohibit exclusive contracts across the board, it could also hurt Rappi.
Macro risks: FX volatilities, lower GDP growth and high unemployment would reduce the propensity to spend.