
Revenue
$85.00M
2024
Valuation
$450.00M
2024
Funding
$450.00M
2022
Growth Rate (y/y)
118%
2024
Revenue
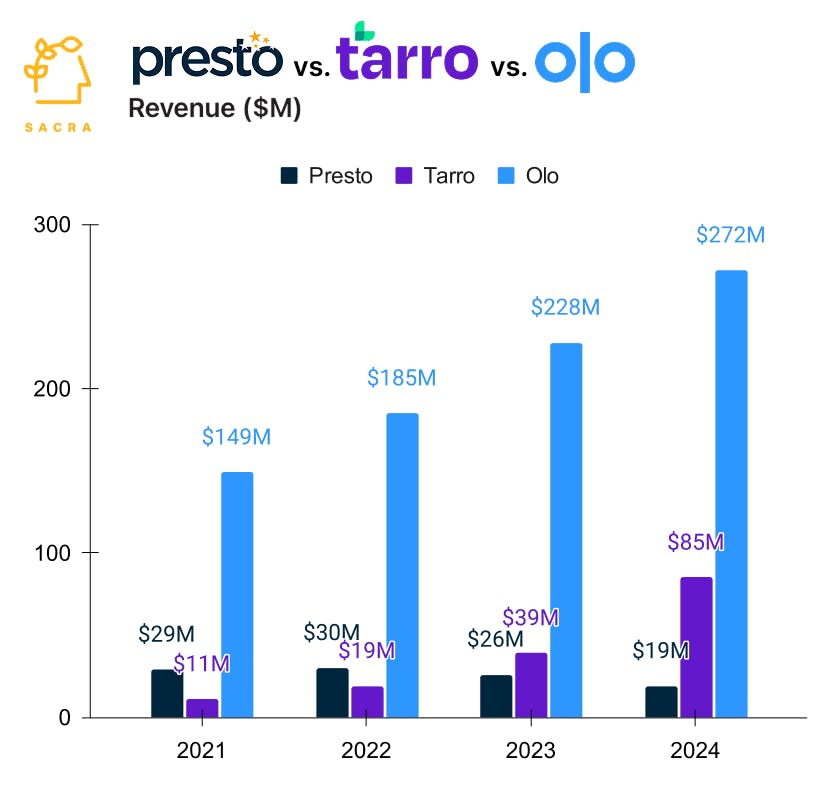
As their customer base has grown to 3,500 restaurants across delivery & takeout-heavy cuisines Chinese, sushi & pizza, Sacra estimates Tarro reached an $85M revenue run rate at the end of 2024, accelerating to 118% YoY growth with ~50% gross margin.
Tarro generates revenue through three primary channels: phone ordering services (saving restaurants an average of $810 in monthly labor costs), delivery services (launched in November 2024 with 300+ initial customers), and SMS marketing solutions ($8,500 annually per restaurant).
Compare to AI voice ordering competitor Olo (NYSE: OLO) at at $272M revenue (+19% YoY) with 55% gross margin and 700 customers for $389K ACV, SoundHound (NASDAQ: SOUN) at $67M revenue (+46% YoY) with 49% gross margin and 200 customers for $335K ACV, and Presto (taken private in January) at $19M revenue (-35% YoY) with 6% gross margin, which eliminated its pay-at-table business (90% of revenue) in 2024, pivoting to focus on voice ordering.
Valuation & Funding
Tarro was valued at $450M (41x multiple on ~$11M ARR) when growth private equity funds Integrity Capital Partners and Cohesive Capital Partners took a minority position in 2022.
Product
Founded in 2012, Tarro found product-market fit in 2015 with software that re-routes phone-in orders to Chinese restaurants in the U.S to a 24/7 call center in the Philippines, giving small, family restaurants access to an always-on, English-speaking remote assistant.
The platform combines AI technology with human agents to manage restaurant phone orders, handling everything from order taking to payment processing. When a customer calls, they're connected to a Tarro agent within 4 seconds who can take their order, make personalized recommendations, and ensure accurate details - all while maintaining a natural conversation flow.
Tarro has since expanded to offer an integrated delivery service and SMS marketing platform. The delivery service allows restaurants to fulfill orders without relying on third-party apps, while the marketing component enables targeted SMS campaigns to drive repeat business. All three services work together through a unified dashboard where restaurant owners can manage their operations, track performance, and adjust their offerings.
The platform particularly resonates with independent restaurant owners who want to maintain direct relationships with their customers while reducing operational complexity and labor costs.
Business Model
Tarro is a technology-enabled services company that helps independent restaurants increase revenue and reduce costs through AI-powered phone ordering, delivery management, and SMS marketing solutions. The company generates revenue through usage-based pricing for its phone ordering service and delivery operations.
Tarro lands inside restaurants with outsourced phone order-takers who are 5-10% cheaper than domestic labor, and they expand by selling into additional services like marketing ($8,500/year) and delivery services launched in September 2024 (effective take rate of ~15% vs. the 20-30% commission of Uber Eats or DoorDash)—with an average revenue per customer of $24K.
The company's core phone ordering service combines AI with human agents to handle customer calls in under 4 seconds with 99.5% accuracy, charging restaurants only when orders are placed. This helps restaurants save 5-10% on labor costs while increasing order volume by an average of 13%.
Tarro's delivery service integrates with phone ordering and enables restaurants to offer delivery without relying on expensive third-party apps, saving customers an average of $10 per order compared to platforms like DoorDash.
While recent "Shopify for restaurants" SaaS like ChowNow (General Catalyst, $94M raised) and Lunchbox (Coatue, $72M raised) focused on giving restaurants websites with online ordering & delivery to own and grow revenue through digital, the next wave of vertical SaaS built on voice AI —companies like Tarro, SoundHound, Presto and Hi Auto—look to save restaurants that run at 3-5% margins $30,000+ in labor costs per year, as a wedge into selling in automation across the stack.
Competition
Tarro operates in the restaurant technology and services market, competing across three key segments: phone ordering/virtual staff, delivery infrastructure, and marketing automation.
Virtual staff and phone ordering
The primary competitors in this space are traditional BPO providers and newer AI-only solutions. Companies like [24]7.ai and Concentrix offer human agent services, while pure AI players like Presto Voice focus on automated ordering. Tarro's hybrid approach of AI-assisted human agents positions it between these extremes, claiming higher accuracy (99.5%) than AI-only solutions while maintaining lower costs than traditional BPOs.
Restaurant delivery infrastructure
DoorDash dominates this space with 67% market share, followed by Uber Eats and Grubhub. These platforms charge restaurants significant commissions (typically 15-30%) and control the customer relationship. Toast and Olo provide white-label delivery infrastructure but focus primarily on enterprise clients. Tarro's model of providing delivery infrastructure while letting restaurants maintain direct customer relationships offers an alternative approach, particularly appealing to independent restaurants seeking to avoid high marketplace fees.
Restaurant marketing automation
This segment includes both general marketing platforms like Mailchimp and restaurant-specific solutions from Toast and Square. Traditional agencies and part-time marketing staff also compete here. Tarro's integration of marketing with its ordering and delivery systems, plus its focus on SMS marketing with claimed 98% open rates, differentiates it from standalone marketing solutions. The company's strategy of offering marketing services free for the first year ($8,500 value) suggests an emphasis on cross-selling across its product suite.
TAM Expansion
Tarro has tailwinds from the digitization of restaurant operations and growing demand for integrated technology solutions, with opportunities to expand into broader restaurant management services and enterprise solutions.
Digital transformation of restaurants
The restaurant industry's shift toward digital operations creates significant growth potential for Tarro. With 750,000 restaurants in the US and 90% having fewer than 50 employees, there's substantial room to expand beyond their current 3,000 restaurant base. The industry's high failure rate (60% in year one) and labor challenges make Tarro's labor-saving solutions particularly valuable.
Enterprise and multi-location expansion
While Tarro initially focused on independent restaurants, particularly Chinese restaurants, they can expand to serve multi-location operations and larger chains. Their AI-powered system's 99.5% accuracy rate and ability to handle complex orders positions them well for enterprise clients seeking consistent service across locations. The success of clients like Arber's Japanese Hibachi demonstrates Tarro's ability to serve higher-end establishments.
Adjacent service opportunities
Tarro can expand beyond phone ordering and delivery into comprehensive restaurant management solutions. Their SMS marketing service suggests potential for broader customer engagement tools. They could develop inventory management, staffing optimization, and financial analytics products. With their AI capabilities, Tarro could also offer predictive analytics for demand forecasting and menu optimization, addressing the thin margins (5-10%) that challenge restaurant profitability.
Risks
Cannibalization: Like Scale AI with data labeling, Tarro benefits from the opportunity to dramatically increase its margins by replacing Filipino call center workers ($3-4/hr) with AI ($0.30-0.40/hr), but to pull that off, it must disrupt its own business model (priced as a discount on the cost of labor) and completely refactor its software & people infrastructure (built on an offshoring model).
Third-party platform competition: Major delivery platforms like DoorDash are investing heavily in AI and could replicate Tarro's phone ordering capabilities. These platforms' existing market presence and significantly larger resources could allow them to quickly capture market share. Their established relationships with restaurants and consumers create high barriers for Tarro's delivery service expansion.
News
DISCLAIMERS
This report is for information purposes only and is not to be used or considered as an offer or the solicitation of an offer to sell or to buy or subscribe for securities or other financial instruments. Nothing in this report constitutes investment, legal, accounting or tax advice or a representation that any investment or strategy is suitable or appropriate to your individual circumstances or otherwise constitutes a personal trade recommendation to you.
This research report has been prepared solely by Sacra and should not be considered a product of any person or entity that makes such report available, if any.
Information and opinions presented in the sections of the report were obtained or derived from sources Sacra believes are reliable, but Sacra makes no representation as to their accuracy or completeness. Past performance should not be taken as an indication or guarantee of future performance, and no representation or warranty, express or implied, is made regarding future performance. Information, opinions and estimates contained in this report reflect a determination at its original date of publication by Sacra and are subject to change without notice.
Sacra accepts no liability for loss arising from the use of the material presented in this report, except that this exclusion of liability does not apply to the extent that liability arises under specific statutes or regulations applicable to Sacra. Sacra may have issued, and may in the future issue, other reports that are inconsistent with, and reach different conclusions from, the information presented in this report. Those reports reflect different assumptions, views and analytical methods of the analysts who prepared them and Sacra is under no obligation to ensure that such other reports are brought to the attention of any recipient of this report.
All rights reserved. All material presented in this report, unless specifically indicated otherwise is under copyright to Sacra. Sacra reserves any and all intellectual property rights in the report. All trademarks, service marks and logos used in this report are trademarks or service marks or registered trademarks or service marks of Sacra. Any modification, copying, displaying, distributing, transmitting, publishing, licensing, creating derivative works from, or selling any report is strictly prohibited. None of the material, nor its content, nor any copy of it, may be altered in any way, transmitted to, copied or distributed to any other party, without the prior express written permission of Sacra. Any unauthorized duplication, redistribution or disclosure of this report will result in prosecution.