
Revenue
$30.00M
2021
Valuation
$5.00B
2022
Funding
$632.00M
2022
Growth Rate (y/y)
200%
2021
Revenue
We estimate that Cockroach Labs made $30M in 2021, a 200% increase from 2020. In the last two years, its revenue has grown at a CAGR of 140%. Its core product CockroachDB is open-source, and Cockroach Labs makes money in two ways. One is by selling backup, 24/7 support, integration services, and other premium features to its enterprise customers who self-host CockroachDB. The other is SaaS-style revenue from customers who use its fully managed cloud database.
While most of the revenue comes from self-hosted customers, the cloud business is growing faster, with 500% growth QoQ in Q4 2021, and nearly 50% of customers are now using the cloud database product. Geographically, Cockroach Labs is seeing strong demand from EMEA, with revenue growing 600% in Q1 2022 and expected to reach 20% of total revenue in 2022.
Valuation & Funding
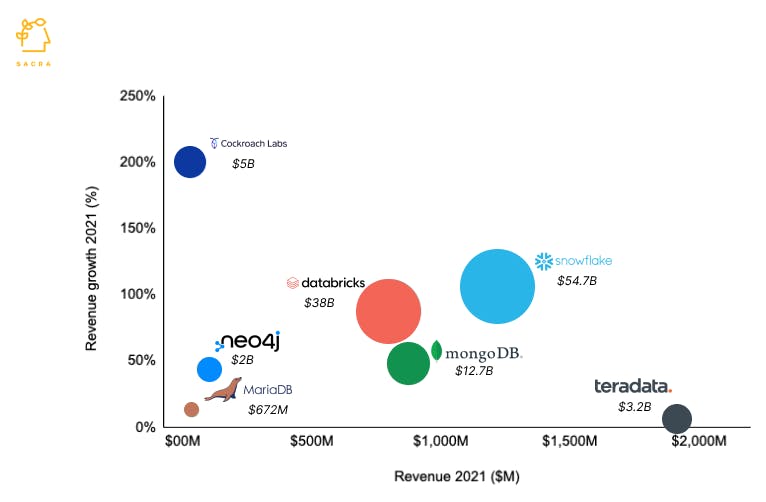
Note: All information as per publicly available data. The size of the bubble indicates valuation.
Cockroach Labs has raised $632M from Greenoaks, Benchmark, Index Ventures, and Redpoint Ventures. It was last valued at $5B, with a valuation/revenue multiple of 166x. Its revenue multiple is much higher than publicly listed database management companies such as MongoDB (14.5x), Oracle (4.4x), and Snowflake (45x) and private companies such as Databricks (47.5x) and MariaDB (19x). Part of the reason for its high valuation is that the cloud database market is expected to grow to $60B by 2024, 1.5X its current size, and among the cloud database companies, Cockroach Labs is growing the fastest.
Business Model
Cockroach Labs sells CockroachDB, an open-source cloud-hosted relational database that provides high uptime and fast data availability by spreading the database clusters worldwide.
Companies can self-host CockroachDB Core open-source database on their cloud infrastructure for free. Cockroach Labs commercializes it by gating premium features and customer support that it sells through an enterprise license. However, the cost of engineers and the cloud infrastructure required to run CockroachDB means companies of only a certain size can afford it . This reduces TAM and indexes revenue to how many enterprise contracts it can sell.
To capture the upside of developers moving more of their production work to the cloud, Cockroach Labs offers two fully managed database as a service offerings, CockroachDB Dedicated and CockroachDB Serverless. Cockroach Labs charges customers SaaS-style usage-linked fees based on how many nodes they need and for how long. Developers get access to enterprise-grade database features without the upfront cost of setting up cloud infrastructure.
As production databases are mission-critical, companies are reluctant to switch providers. Hence, Cockroach Labs GTM anchors on making it easy for developers to try its database. On the enterprise side, it tweaks the open-source Core to run off a laptop without setting up a full cloud infrastructure, which serves as the top of the funnel for getting the high frequency of use customers. For its cloud offerings, it has a bottom-up sales motion where developers can use the base version for free forever without even entering credit card information. When they hit scale, they can put a credit card down and pay for what they use.
Product
A company can have only a certain number of database servers that serve its geographically dispersed users, and the further a user is away from the database, the longer it takes for information to reach them, constrained by network speeds. Thus, if a server is on the East Coast of the US, a user in New York will receive data faster than a user in Europe.
Companies solve this problem by replicating their databases across key geographies and localizing them so that the most useful data is closer to users. However, this needs considerable technical know-how and ongoing administration to make it work reliably, as traditional relational databases are designed for single servers, not for scaling horizontally across different servers.
Cockroach Labs got an initial product-market fit by providing an out-of-the-box solution for companies to scale relational databases across multiple servers and keeping useful data closest to users with its multi-region database architecture.
CockroachDB offers three advantages over traditional relational databases:
- It auto-replicates data so that databases are in sync with each other.
- If one version goes down, the next can take over, providing higher uptime.
- Developers can localize data for specific geographies so data related to New York users can easily be stored in the East Coast data center.
As an open-source software under Business Source License (BSL), anyone can use CockroachDB for free but cannot repackage it and sell it to their customers.
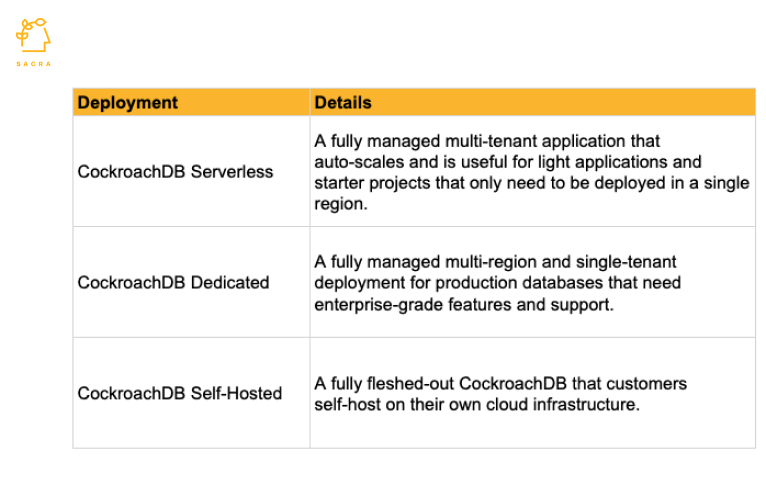
Cockroach Labs offers three types of deployments of CockroachDB.
In October 2025, Cockroach Labs entered an OEM partnership with IBM to deliver CockroachDB PostgreSQL for IBM across hybrid environments. The agreement extends CockroachDB to IBM LinuxONE, IBM Z, Power Systems, Red Hat OpenShift, and IBM Cloud, enabling active-active resilience and data locality with PostgreSQL compatibility. The collaboration is positioned for AI workloads, with pgvector support and CDC streaming into watsonx.data.
Competition
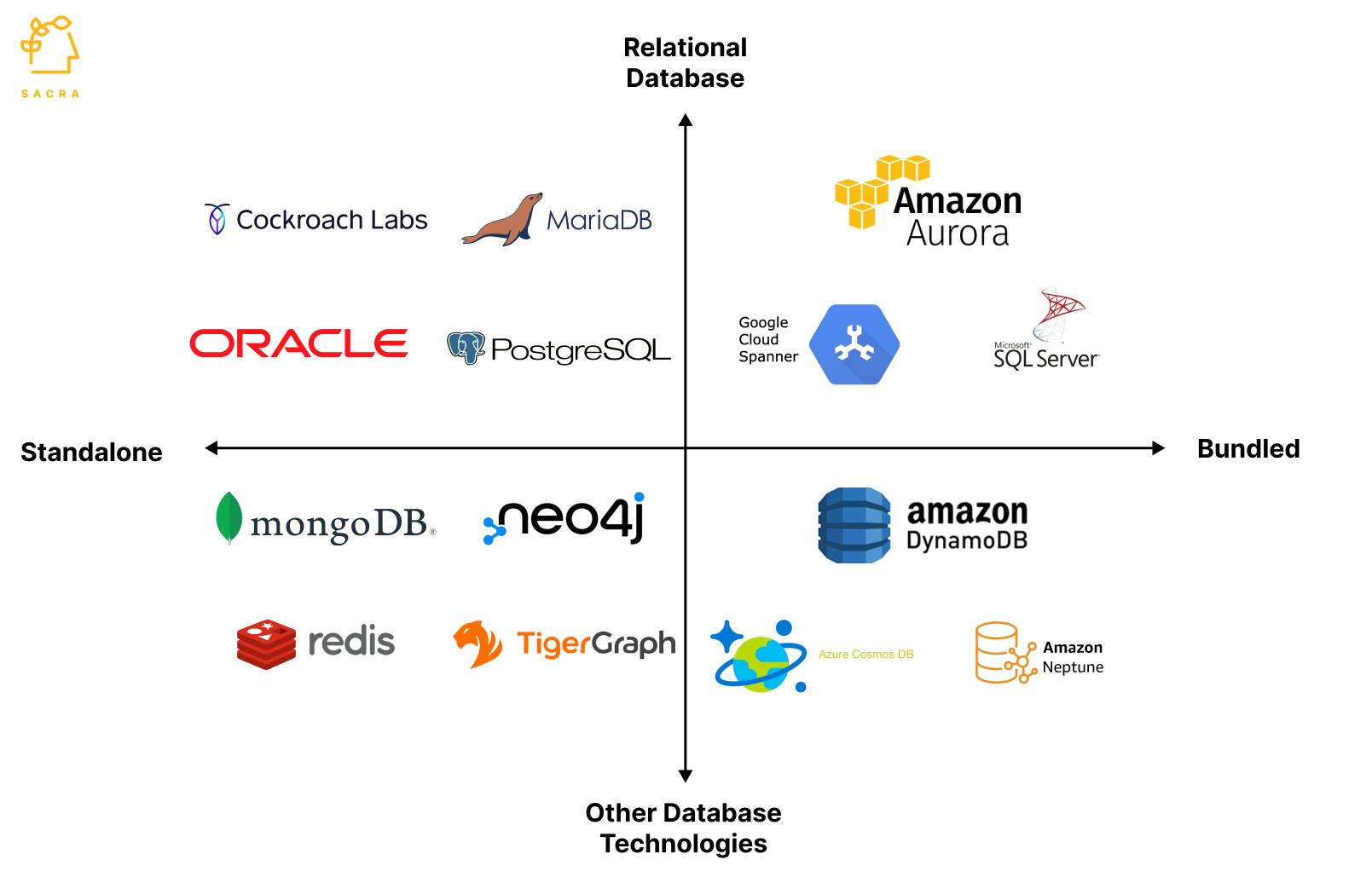
Cockroach Labs competes in a crowded relational database market with large incumbent players like Oracle and Microsoft, open-source solutions like PostgresSQL and MySQL, and cloud service providers like AWS and Microsoft Azure. It also competes with other technologies like NoSQL database (MongoDB) and Graph database (Neo4J), growing faster than relational databases.
Incumbent relational database companies
Oracle, the original relational database company, has lost market share consistently over the last five years, dropping from 36% in 2017 to 20.6% in 2021, as its cloud database has grown slowly. Still, it remains a formidable player as many companies, especially those launched pre-2000, are locked into mainframes and Oracle databases, finding it difficult to migrate to the modern cloud. Cloud companies like AWS, Microsoft, and Google have gained market share at the expense of on-prem companies like Oracle, SAP, and IBM and currently have ~55% of the market share.
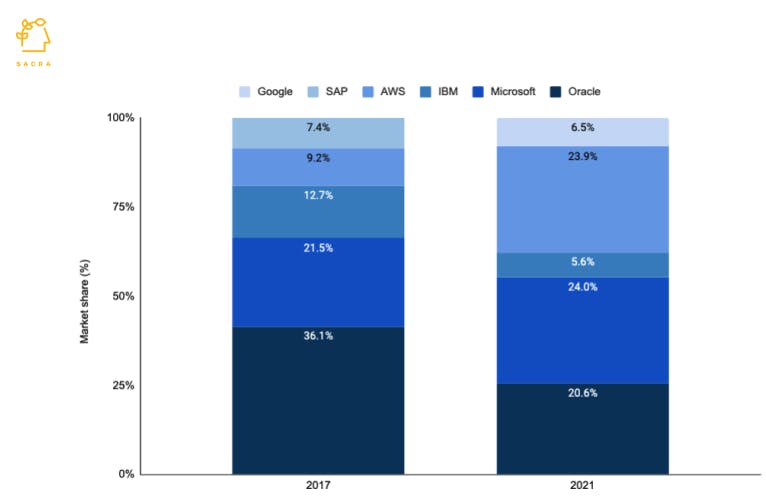
Cloud platforms have gained considerable market share over the last 5 years.
New database technologies
Relational databases are still ~85% of the database market, but NoSQL and Graph databases, with 10% and 5% market shares, respectively, are catching up. Graph databases are the biggest threat to relational databases as they can be 100x-1000x faster but are currently limited by the size of workloads they can process. As they improve to process petabytes of data reliably, they are expected to capture 1/3rd of the market in the next 10 years, with NoSQL growing to 15% and the share of relational databases dropping to 50%.
TAM Expansion
Cockroach Labs' growth is indexed on the production databases shifting from on-prem to cloud, and Cockroach Labs, with its one-of-a-kind open-source distributed database, using this shift to expand its revenue.
Cloud infrastructure growth
Cloud computing spend increased 3x from $105B in 2015 to $320B in 2020 and is expected to grow to $848B in 2025, to reach 16% of the global IT spend as infrastructure software companies index on the cloud for growth. At $40B, the cloud database is already 56% of the database market and is expected to grow to $60B by 2024, cornering 70% of the market, providing a major tailwind to CockroachDB.
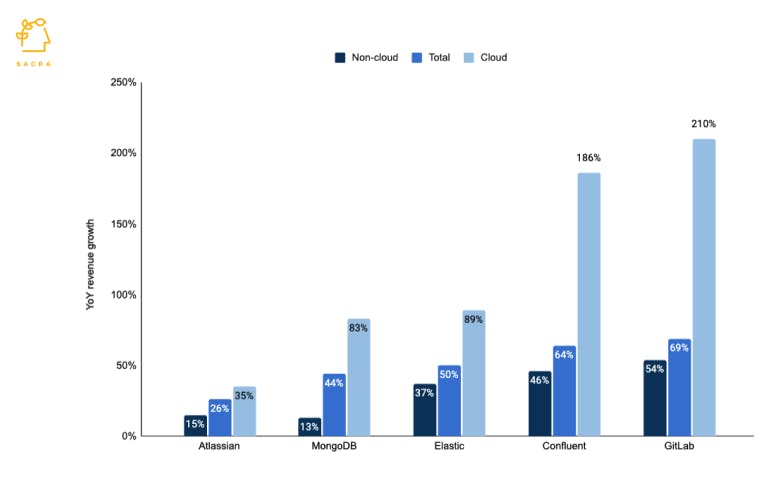
Infrastructure software companies are indexing to the cloud for growth.
Open-source database
Many startups like VoltDB, MemSQL, and NuoDB tried distributed relational databases before Cockroach Labs. Still, they failed to gain traction as, unlike CockroachDB, they weren’t open source. By being open source, customers don’t feel they are being locked into a proprietary architecture by the likes of Oracle or Microsoft. Another open-source database MongoDB has grown at a CAGR of 54% over the last 5 years to gain a 2.5% share of the NoSQL market.
Risks
Bundled databases by cloud platforms
In the last 5 years, all three large cloud platforms - AWS, Microsoft Azure and Google Cloud, have gained market share in the database market. All of them have distributed database offerings similar to CockroachDB and much larger distribution presence with developers which can outpace Cockroach Labs bottom up developer-focused sales motion.
High valuation
CockroachLabs is valued at 166x revenue which will have implications for future investors to generate a sizable return and Cockroach Labs’ ability to recruit high quality talent for whom it may be too richly valued for any upside in their next job.
Fundraising










News
DISCLAIMERS
This report is for information purposes only and is not to be used or considered as an offer or the solicitation of an offer to sell or to buy or subscribe for securities or other financial instruments. Nothing in this report constitutes investment, legal, accounting or tax advice or a representation that any investment or strategy is suitable or appropriate to your individual circumstances or otherwise constitutes a personal trade recommendation to you.
This research report has been prepared solely by Sacra and should not be considered a product of any person or entity that makes such report available, if any.
Information and opinions presented in the sections of the report were obtained or derived from sources Sacra believes are reliable, but Sacra makes no representation as to their accuracy or completeness. Past performance should not be taken as an indication or guarantee of future performance, and no representation or warranty, express or implied, is made regarding future performance. Information, opinions and estimates contained in this report reflect a determination at its original date of publication by Sacra and are subject to change without notice.
Sacra accepts no liability for loss arising from the use of the material presented in this report, except that this exclusion of liability does not apply to the extent that liability arises under specific statutes or regulations applicable to Sacra. Sacra may have issued, and may in the future issue, other reports that are inconsistent with, and reach different conclusions from, the information presented in this report. Those reports reflect different assumptions, views and analytical methods of the analysts who prepared them and Sacra is under no obligation to ensure that such other reports are brought to the attention of any recipient of this report.
All rights reserved. All material presented in this report, unless specifically indicated otherwise is under copyright to Sacra. Sacra reserves any and all intellectual property rights in the report. All trademarks, service marks and logos used in this report are trademarks or service marks or registered trademarks or service marks of Sacra. Any modification, copying, displaying, distributing, transmitting, publishing, licensing, creating derivative works from, or selling any report is strictly prohibited. None of the material, nor its content, nor any copy of it, may be altered in any way, transmitted to, copied or distributed to any other party, without the prior express written permission of Sacra. Any unauthorized duplication, redistribution or disclosure of this report will result in prosecution.