
Revenue
$153.40M
2023
Valuation
$1.15B
2023
Funding
$435.00M
2022
Growth Rate (y/y)
69%
2023
Revenue
Sacra estimates that Betterment grew revenue to $153M in 2023, up 69% from $91M in 2022. The primary cause of Betterment's revenue acceleration, after growing just 11% year-over-year in 2022, was increased AUM via deposits both to their core robo-advisor product and to their Betterment Reserve high-yield cash account.
Betterment's AUM continued growing through 2025, reaching $55B+ by February 2025 and $65B+ by November 2025, with the customer base expanding to 1M+ customers by year-end. The company grew its AUM from an average of $30.7B in 2022 to an average of $38.35B in 2023, while at the same time benefitting from the improved unit economics of their cash accounts vs. their traditional robo-advisor accounts. Cash accounts allow Betterment to earn about 0.40% per dollar of AUM vs. 0.25% per dollar of AUM on their robo-advisor product.
As interest rates rose from the spring of 2022 through the summer of 2023, the effect was to significantly increase the amounts that neobanks like Betterment and Wealthfront could earn on their deposits, creating a way for them to acquire customers by passing some of those earnings on.
Effective January 5, 2026, Betterment changed its Digital offering pricing structure to a $5/month flat fee ($60/year), which adjusts to the original 0.25% fee when account balances reach $24,000+ or clients enable $200+/month recurring deposits.
Valuation & Funding
Based on 2021 data, the company traded at a 16x revenue multiple, with $81M in revenue against a $1.3B valuation.
The company has raised $435M across 11 funding rounds, with backing from prominent investors including Bessemer Venture Partners, Menlo Ventures, and Francisco Partners. The most recent funding included investments from Treasury and Aflac Ventures, positioning Betterment as a significant player in the fintech sector.
Business Model
Betterment is a robo-advisor that automatically decides an investor's asset allocation based on their preferences, financial goals, and risk appetite. The investment experience is offered from within its app and website, with an investor-friendly user interface. Unlike other investment firms, Betterment only invests in ETFs, which coupled with automation and digital-only service, allows them to charge a low management fee.
Betterment found product-market fit by providing DIY investors with a cost-effective investment service. These consumers typically found traditional investment firms too expensive. Later, Betterment added products for seasoned investors, SMBs, and investment advisors. It also offers neobank-like products such as interest-bearing cash accounts and debit cards to draw in young customers who are not interested in investing.
It has five revenue streams:
Portfolio management fees: This is the largest component of its revenue. It has two plans: a digital-only investment service with a 0.25% fee and no minimum balance and hybrid investment service that provides calls with investment advisors at 0.4% fees and a $100k minimum balance.
Interchange: Betterment earns an interchange fee every time its debit cards are used. It offers a Visa debit card through nbkc Bank.
Partner banks: For Betterment's cash reserve product, it deposits funds with partner banks for which it earns a commission.
Advice packages: Betterment sells phone consultations with investment professionals that start at $299.
Employers: Betterment offers a 401(k) product to SMBs for their employees, for which it charges SMBs a SaaS-style monthly fee.
Product
Betterment's products can be categorized into three buckets based on who uses them: individuals, SMBs, and advisors.
While the individual-focused products are designed to help them invest, SMB and advisor products are intended for them to offer Betterment as an investment service to their employees and clients.
When onboarding customers, Betterment asks for their preferences and goals (retirement planning, buying a home, kids' college tuition, etc.), then sets up their monthly investment and matches them with its pre-built portfolio options.
Once set up, its algorithms automatically invest monthly deposits and rebalance the portfolios to match customers' financial goals. In November 2025, Betterment launched self-directed investing, enabling commission-free trading of thousands of stocks and ETFs alongside its automated portfolios. The platform includes Tax Impact Preview, which shows pre-trade tax implications including capital gains and wash sale warnings.
Competition
Traditional incumbents
The US investment management market is becoming saturated with fintechs and legacy players offering their customers low-cost, robo-advisor investment services. Betterment competes with traditional players like Charles Schwab and Vanguard, which started rival robo-advisor services after the launch of Betterment. By leveraging their vast network and offering lower fees than Betterment, they have become the two largest robo-advisors by AUM.
Fintech robo-advisors
Apart from other robo-advisors such as Wealthfront and Personal Capital, Betterment also competes with fintechs such as Acorns (financial wellness), Chime (neobank), and Robinhood (DIY investment). The number of robo-advisor account holders grew to 3.5M in 2021, 2X from 2018, but their growth is expected to slow down to 10.4% YoY to reach 5.2M by 2025.
Specialist robo-advisors
Betterment acquired Ellevest's automated investing business in early 2025, eliminating a specialist competitor that focused on women investors. Other specialist robo-advisors such as Blooom (IRA and 401k) continue to cater to specific use cases and compete for niche segments of the market.
TAM Expansion
New products
One of the ways for Betterment to grow is to offer more financial products to scale its AUM. It recently started offering student loan management service to SMBs for their employees post its acquisition of Gradvisor. Similarly, it acquired Makara, a robo-advisor for cryptocurrencies to give individuals and advisors access to crypto portfolios.
In November 2025, Betterment launched self-directed investing with commission-free stock and ETF trading, targeting the 75%+ of its customers who already held self-directed investments off-platform. Apart from investment products, it can consider credit cards, lending, and insurance, either directly or acting as a distributor for others.
New automation features
Another way for Betterment to grow is to expand automation beyond investment products to cash management products.
It can scan customer's bank accounts to remove non-useful subscriptions, pay bills automatically, manage their budgets, and help them improve their savings. While this may not directly increase AUM, it creates a stickier customer experience, which can reduce churn and help Betterment attract new customers.
Acquisitions
Betterment acquired Ellevest's automated investing business in February 2025, transferring approximately $1.1B in AUM from ~70,000 clients in mid-April 2025. In May 2025, Betterment acquired Rowboat Advisors for its direct indexing and tax optimization technology, with plans to integrate it into Betterment Advisor Solutions in 2H 2025 and preview direct indexing capabilities in 2026.
Advisor and SMB expansion
Betterment Advisor Solutions launched an all-digital Solo 401(k) product in February 2025, built on the same recordkeeping system powering Betterment at Work, targeting independent advisors and their self-employed clients with paperless opening and no setup fees. In September 2025, Betterment at Work partnered with First Citizens Wealth to provide 401(k) solutions to First Citizens' SMB and mid-market clients, including SVB and CIT divisions, with Betterment serving as plan recordkeeper.
Risks
Lower interest rates
Betterment is one of the neobanks that benefitted greatly in 2023 from the rise in interest rates driving up the yields that they could both collect from deposits and offer to their users. Betterment's 69% revenue growth in 2023 was a testament to this—but the problem is that interest rates won't stay high forever. By the time they come back down, Betterment will either have to have new lines of business that can pick up the slack, or they will have to convince their new users to stick around and invest and spend with them in the long-term.
Lack of differentiation
Betterment acquired users rapidly in the early years by offering a low cost investment service to DIY investors who found traditional investment management firms too expensive. However, now with traditional investment firms, neobanks, and other robo-advisor firms offering nearly identical products at similar management fees, there isn’t much to differentiate one robo-advisor app from another. As the product becomes more commoditized, Betterment may struggle to acquire customers for its core investment service business.
Fundraising
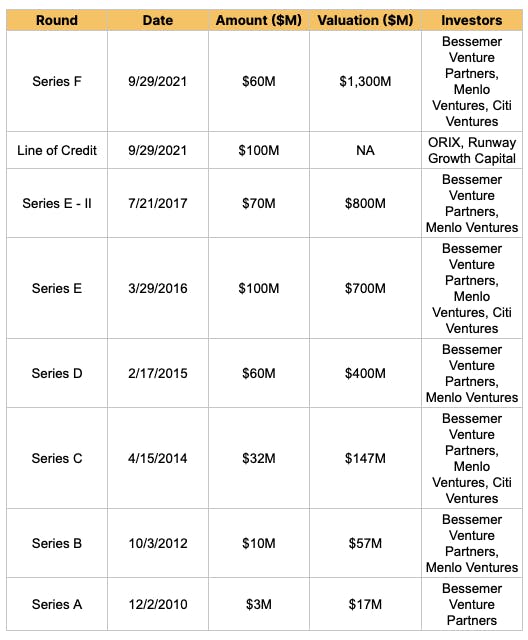








News
DISCLAIMERS
This report is for information purposes only and is not to be used or considered as an offer or the solicitation of an offer to sell or to buy or subscribe for securities or other financial instruments. Nothing in this report constitutes investment, legal, accounting or tax advice or a representation that any investment or strategy is suitable or appropriate to your individual circumstances or otherwise constitutes a personal trade recommendation to you.
This research report has been prepared solely by Sacra and should not be considered a product of any person or entity that makes such report available, if any.
Information and opinions presented in the sections of the report were obtained or derived from sources Sacra believes are reliable, but Sacra makes no representation as to their accuracy or completeness. Past performance should not be taken as an indication or guarantee of future performance, and no representation or warranty, express or implied, is made regarding future performance. Information, opinions and estimates contained in this report reflect a determination at its original date of publication by Sacra and are subject to change without notice.
Sacra accepts no liability for loss arising from the use of the material presented in this report, except that this exclusion of liability does not apply to the extent that liability arises under specific statutes or regulations applicable to Sacra. Sacra may have issued, and may in the future issue, other reports that are inconsistent with, and reach different conclusions from, the information presented in this report. Those reports reflect different assumptions, views and analytical methods of the analysts who prepared them and Sacra is under no obligation to ensure that such other reports are brought to the attention of any recipient of this report.
All rights reserved. All material presented in this report, unless specifically indicated otherwise is under copyright to Sacra. Sacra reserves any and all intellectual property rights in the report. All trademarks, service marks and logos used in this report are trademarks or service marks or registered trademarks or service marks of Sacra. Any modification, copying, displaying, distributing, transmitting, publishing, licensing, creating derivative works from, or selling any report is strictly prohibited. None of the material, nor its content, nor any copy of it, may be altered in any way, transmitted to, copied or distributed to any other party, without the prior express written permission of Sacra. Any unauthorized duplication, redistribution or disclosure of this report will result in prosecution.