
Valuation
$2.12B
2025
Funding
$641.25M
2025
Valuation & Funding
Agility Robotics closed a $400 million Series C in March 2025, valuing the company at about $2.12B.
The company has raised approximately $641 million in total funding across multiple rounds. Key investors include DCVC, Playground Global, Amazon Industrial Innovation Fund, NVentures (NVIDIA's venture arm), Humanoid Global Holdings, Sony Innovation Fund, and Safar Partners.
Product
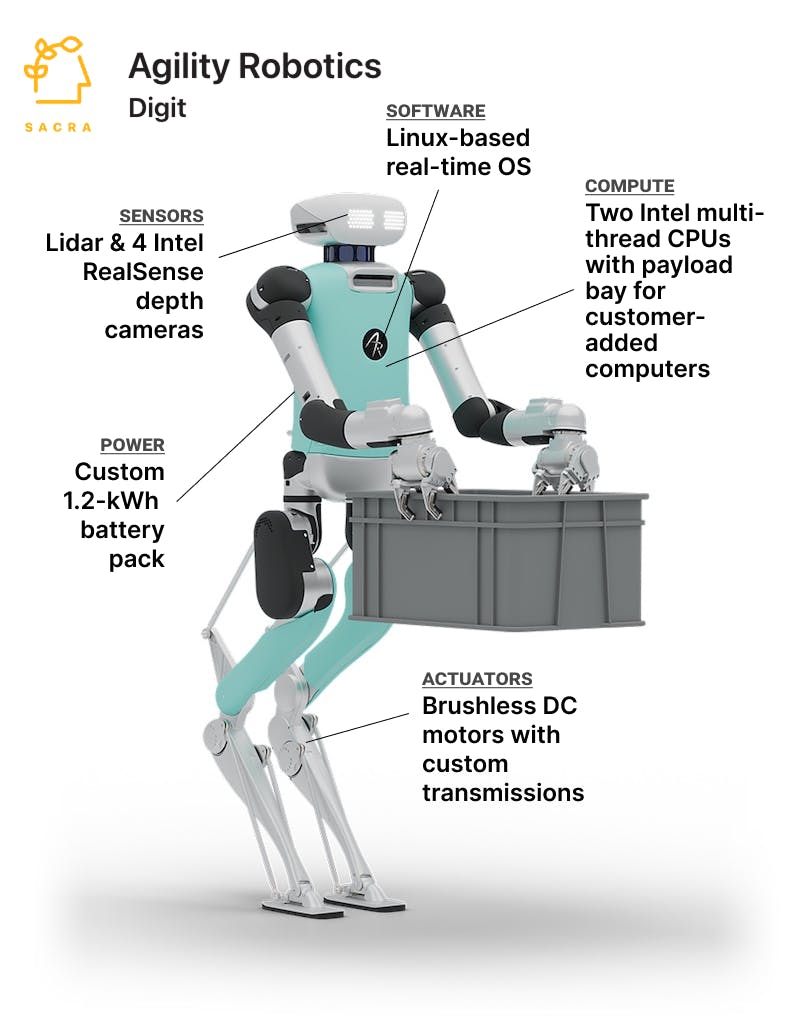
Agility Robotics's Digit is a 5-foot-9 humanoid robot designed to work alongside humans in warehouse and logistics environments. The robot walks on two spring-loaded legs and features two arms capable of lifting 35 pounds, allowing it to handle standard warehouse totes and packages.
The robot navigates using cameras, lidar, and an inertial measurement unit that provide 360-degree vision and balance control. This sensor suite enables Digit to walk over ramps, curbs, and dock plates that would stop wheeled robots, while maintaining stability in dynamic warehouse environments.
A typical workflow involves Digit identifying totes placed on shelves by mobile robots or human workers, gripping them with specialized mitt-like end effectors, walking to conveyor systems, and placing items for further processing. The robot operates for 2-3 hours of heavy use before returning to autonomous charging docks, with battery life extending up to 8 hours for lighter tasks.
The Agility Arc cloud platform connects Digit fleets to customer warehouse management systems, enabling over-the-air skill updates, automated charging schedules, and performance analytics. Integration typically takes hours or days rather than weeks, with work-cell kits including safety systems that allow deployment without traditional robotic fencing.
Business Model
Agility operates a hybrid B2B model combining direct robot sales with robotics-as-a-service subscriptions. The RaaS model reduces customer capital expenditure barriers while creating recurring revenue streams tied to robot utilization and performance.
Direct sales target customers ready for immediate ownership, typically priced around $150,000 per unit including integration support. RaaS contracts provide robots, maintenance, software updates, and support for monthly fees that align costs with operational benefits, making the technology accessible to smaller operations.
The business leverages a vertically integrated manufacturing approach through its Salem, Oregon RoboFab facility. The factory uses a modular assembly system called ARMS that can scale production from hundreds to 10,000 units annually by replicating standardized production cells for legs, arms, torsos, and actuators.
Software represents an increasingly important margin driver through the Arc platform, which provides fleet management, workflow orchestration, and integration capabilities. This creates switching costs and enables expansion revenue as customers deploy additional robots or add new capabilities to existing fleets.
Competition
Vertically integrated giants
Boston Dynamics leverages its partnership with Hyundai to deploy Atlas humanoid robots across automotive manufacturing facilities, with plans for tens of thousands of units. The company's Stretch mobile manipulator has secured a 1,000-unit agreement with DHL, demonstrating scale ambitions beyond traditional high-cost, limited-deployment models.
Tesla's Optimus program targets 10,000 units in 2025 and 50,000 in 2026, leveraging automotive supply chain advantages and AI capabilities from its vehicle autonomy programs. The strategy mirrors Tesla's approach with electric vehicles, starting with internal factory deployment before expanding to external sales.
Amazon's internal robotics division develops competing automation solutions for its own fulfillment network while potentially limiting Agility's access to the largest logistics customer in the market.
Specialized humanoid startups
Figure AI has raised significant funding to develop general-purpose humanoid robots with partnerships across automotive and logistics sectors. The company focuses on AI-driven manipulation capabilities and has demonstrated integration with OpenAI's language models for more intuitive robot control.
Apptronik targets similar warehouse and logistics applications with its Apollo humanoid platform, emphasizing modular design and rapid deployment capabilities. The company competes directly on use cases like tote handling and palletizing that represent Digit's core market.
Traditional automation incumbents
Established industrial automation companies like ABB, KUKA, and Fanuc are expanding beyond fixed robotic arms into mobile manipulation systems. These players bring deep manufacturing relationships, global service networks, and proven reliability records that could challenge humanoid robot adoption in structured environments.
Warehouse automation specialists including Locus Robotics, 6 River Systems, and GreyOrange offer alternative approaches to goods-to-person and automated picking that compete for the same labor cost savings and efficiency improvements that drive humanoid robot adoption.
TAM Expansion
New products
Enhanced Digit variants with extended 4-hour runtime, autonomous self-docking, and higher payload capacity up to 70 pounds open addressable markets in palletizing, truck loading, and manufacturing line-feeding applications. These upgrades leverage the same core platform while expanding into tasks requiring greater strength and endurance.
The Arc cloud platform creates opportunities for software-driven revenue expansion through fleet orchestration capabilities that manage mixed automation systems including autonomous mobile robots, conveyors, and collaborative robots. This positions Agility as an automation integration layer rather than just a robot supplier.
Robots-as-a-service pricing models lower barriers for small and medium warehouse operations that cannot justify large capital expenditures but face similar labor challenges as enterprise customers. This dramatically expands the addressable customer base beyond Fortune 500 logistics operations.
Customer base expansion
Third-party logistics providers and retailers facing 30-40% annual warehouse labor turnover represent natural expansion targets for tote recycling, palletizing, and returns sorting applications. These tasks account for approximately 25% of labor hours in US distribution centers and align with Digit's current capabilities.
Manufacturing environments offer significant growth potential for assembly line feeding, machine tending, and end-of-line palletizing applications that mirror existing motion primitives. The global factory automation market projected at $415 billion in 2027 provides substantial room for expansion beyond pure logistics applications.
Brownfield retrofits represent a key advantage for humanoid robots that can navigate existing aisles, mezzanines, and stairs without requiring multimillion-dollar facility redesigns that fixed automation systems demand.
Geographic expansion
The modular ARMS manufacturing system enables replication of production capabilities in Europe or Asia as demand justifies regional facilities. This approach reduces shipping costs and delivery times while supporting local service requirements for international deployments.
GXO's global footprint across Europe, Latin America, and Asia-Pacific provides established channels for international expansion without building independent field service organizations in every market. This partnership model accelerates geographic reach while reducing operational complexity.
Japan and Korea represent attractive early international markets due to aging workforce demographics, government subsidies for robotic mobility solutions, and cultural acceptance of automation technologies in workplace environments.
Risks
Manufacturing scale: Meeting demand requires scaling production from hundreds to thousands of units annually while maintaining quality and cost targets. The shift from prototype assembly to mass manufacturing introduces operational risks that could affect delivery timelines and unit economics.
Technology commoditization: As humanoid robotics technology matures, differentiation in hardware design and basic manipulation capabilities may erode, reducing pricing power and shifting competition toward cost rather than performance.
Customer concentration: Reliance on early anchor customers like Amazon and GXO creates revenue concentration risk, especially if these customers develop internal alternatives or significantly reduce deployment plans due to changing operational priorities or economic conditions.
News
DISCLAIMERS
This report is for information purposes only and is not to be used or considered as an offer or the solicitation of an offer to sell or to buy or subscribe for securities or other financial instruments. Nothing in this report constitutes investment, legal, accounting or tax advice or a representation that any investment or strategy is suitable or appropriate to your individual circumstances or otherwise constitutes a personal trade recommendation to you.
This research report has been prepared solely by Sacra and should not be considered a product of any person or entity that makes such report available, if any.
Information and opinions presented in the sections of the report were obtained or derived from sources Sacra believes are reliable, but Sacra makes no representation as to their accuracy or completeness. Past performance should not be taken as an indication or guarantee of future performance, and no representation or warranty, express or implied, is made regarding future performance. Information, opinions and estimates contained in this report reflect a determination at its original date of publication by Sacra and are subject to change without notice.
Sacra accepts no liability for loss arising from the use of the material presented in this report, except that this exclusion of liability does not apply to the extent that liability arises under specific statutes or regulations applicable to Sacra. Sacra may have issued, and may in the future issue, other reports that are inconsistent with, and reach different conclusions from, the information presented in this report. Those reports reflect different assumptions, views and analytical methods of the analysts who prepared them and Sacra is under no obligation to ensure that such other reports are brought to the attention of any recipient of this report.
All rights reserved. All material presented in this report, unless specifically indicated otherwise is under copyright to Sacra. Sacra reserves any and all intellectual property rights in the report. All trademarks, service marks and logos used in this report are trademarks or service marks or registered trademarks or service marks of Sacra. Any modification, copying, displaying, distributing, transmitting, publishing, licensing, creating derivative works from, or selling any report is strictly prohibited. None of the material, nor its content, nor any copy of it, may be altered in any way, transmitted to, copied or distributed to any other party, without the prior express written permission of Sacra. Any unauthorized duplication, redistribution or disclosure of this report will result in prosecution.